Good listening skills allow project managers to learn about and engage with clients and team members. Effective communication is one of the key competencies in project management and is central for effective collaboration.
At every stage of the project, the manager needs to negotiate with multiple parties.
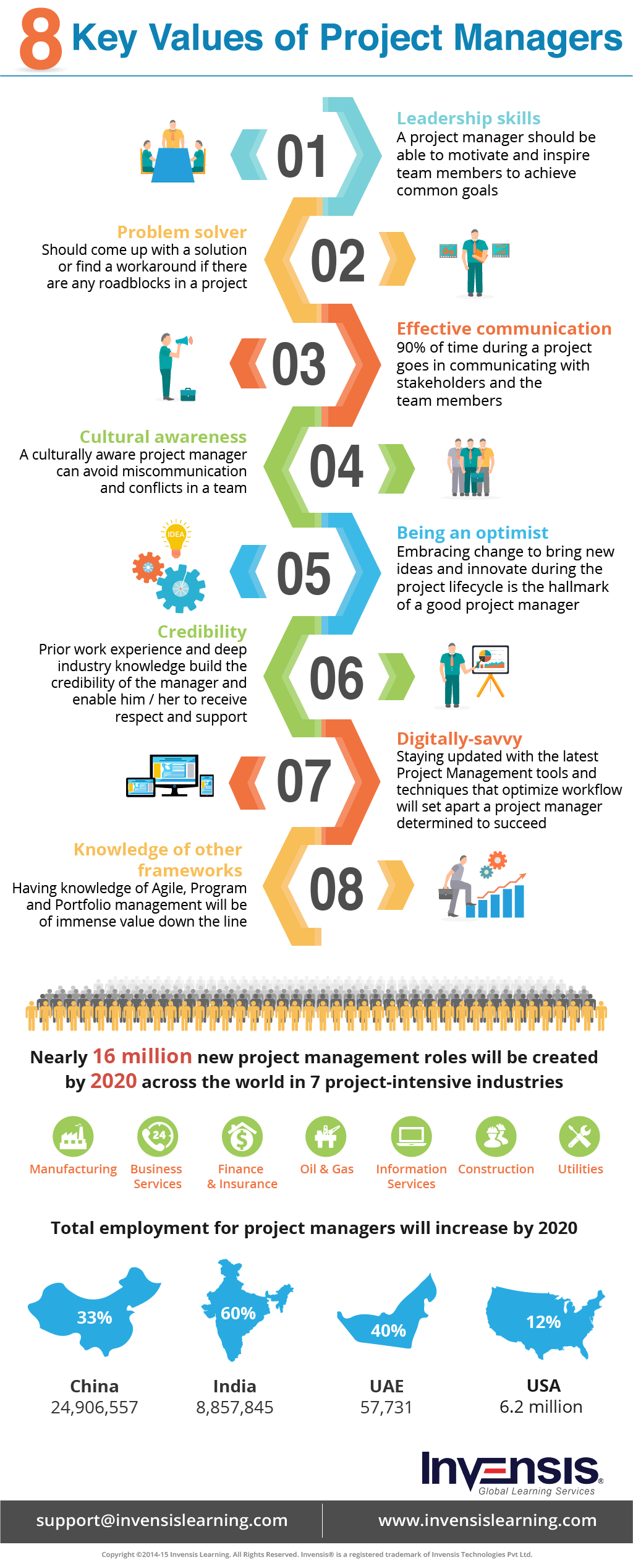
Skills for effective project management. He needs to be able to arrive at decisions that are in the best interest of the project and organization. Here are six essential skills for every project manager: 10 project management key skills:
20 project management skills 1. This also boosts the morale of the team because people enjoy working with one another. There won’t be a single project that hasn’t had its fair share of ups and downs;
Sometimes, you might have to help your team come to a mutual understanding when an argument arises. This is a soft skill you can learn, but project management is probably best suited for those who have a natural tendency toward organization and order. As a project management student, i’m building on the skills i’ve gained through my prior roles and developing new capabilities that will allow me to be successful in my field.
With corporate life and businesses taking the world of industrialization to the next level, there is a great demand for individuals who can pose as mediators and “managers” to successfully transition into this new world we are looking at. Traits of successful project managers. Good leadership will also influence your work.
Project management approaches and methodologies Team members, other departments, leadership, clients…. Teamwork is also said to spark innovation, foster personal growth, and boost creativity.
Project managers aim for clarity and sensitivity and have the ability to speak clearly and concisely with all team members. Updating stakeholders, motivating the team, asking for support on a new direction, or advocating for the project to a new audience. Good project managers lead by example.
This is where it gets messy. This involves setting reasonable expectations, ensuring team members. This is another soft skill that.
Project management is a simple term but it encompasses a wide range of skills. The goal of a leader is to inspire, motivate, and lead the team through various challenges and tasks so that the project schedule is not affected. That’s good news for people who are looking for jobs that allow them to interact with people, solve problems, and put their organizational talents to use.
These individuals possess project management key skills, unlike others, as they. It is the responsibility of the project manager to empower and inspire team members. Here are 11 technical and workplace skills you’ll want to have as a project manager.
This requires a lot of trust on your part and on the part of your team members. It’s impossible to achieve the goals set without team member’s engagement. So, to proceed to the next level of management expertise, a project manager must be able to motivate the team.
Workers may respond better to managers who are able to stay on task, avoid. When you have so many people to manage, communication is key. Project managers must have strong communication skills to be able to convey messages to clients and.
These skills help a project manager to manage the team and lead the team members to work more effectively and efficiently. Successful project managers have excellent leadership skills because you need team members who trust and respect your decisions. From managing resources, to engaging suppliers, to dealing with team conflict, leading a project means.
Influence requires the ability to build trust, foster cooperation, and encourage people to work together. Strong leadership skills are critical for project managers. Successful project managers clearly and effectively disseminate information, communicating in a way that inspires trust and avoids glossing over anything that could cause issues for the project overall.
Technical project management skills 1. The ability to lead a team through all stages of a project is essential. Being able to manage conflicts among your team and clients is an important part of this job.
This soft skill is put to the test continuously during project management. To develop your communication skills, practice being open and honest with your coworkers. They’re the foundation for the soft skills and the way you execute the hard.
Even being able to diffuse tense situations. Below we explore a few key project management skills that recruiters look upon highly and how you can develop them: A project manager leads a projects team using good communication, interpersonal skills, motivational skills, and organization.
These skills are required for building an effective project team and its successful management. It’s the project manager’s job to deal with them while keeping the team happy and productive during the tricky moments. Mastering both of these communication soft skills creates a mutual trust.
Project management skills are the competencies and traits a person needs in order to effectively coordinate a project from start to finish. The ability to manage time and prioritize tasks is an essential characteristic of efficient project managers. In turn, listening aligns directly with good communication.
As a project manager, you might oversee several projects and teams simultaneously. The above list of project management skills misses out on a crucial part of being a pm: Return to the list of project management skills.
Leadership, on the other hand, requires both project management skills and emotional intelligence. They’re cool under pressure, positive, and energetic. As a project manager, you need to work with a lot of different people:
Coaching is a balanced mixture of poise, productivity, team management skills, tutoring, mentoring, and much more. The project manager needs to carefully spend the funds and get the most out of it. 7 essential project management skills 1.
Having interpersonal skills can help you assess a conflict and come up with a solution. They allow leaders to oversee and coordinate. One final soft skill a great pm should have is the ability to get a group of people, who you don’t necessarily have any authority over, to work toward a shared goal.
In 1960, douglas mcgregor developed a leadership theory (mcgregor theory x and theory y) about organization and management in which he represented two opposing perceptions about people in their working environment. He referred to these opposing motivational methods as theory x and theory y management.

MANAGEMENT THEORY THEORY X & THEORY Y Kalpatharu Consulting
Also, the employee is committed to an.

Management theory x and theory y. Let’s break each down and see how they apply in the workplace. Each assumes that the manager’s role is to organize resources, including people, to best benefit the company. Managers only need to play a supportive role to get work from them.
Curiously titled theory x theory y, his theory outlines two opposing views on human behavior in the workplace. And, just like your algebra class, x and y don’t work totally independently, although you can manage in a style that is mostly a theory x or theory y management style. The professional levels of discipline, accountability and.
Theory x and theory y management mindsets impact the way supervisors delegate tasks, design projects and motivate the people they lead. Unfortunately, in the former, employees get turned into mere “cogs in a machine.” Thus, we can say that theory x presents a pessimistic view of employees’ nature and behaviour at work, while theory y presents an optimistic view of the employees’ nature and behaviour at work.
Theory x and theory y of management are unique management styles that focus on different beliefs managers or teams leads have about their employees. Leaders must respond with a participative style of management. He has given two pairs of assumptions about human beings which were implied by the actions of managers in the organization.
Mcgregor's findings favor theory y management, and his book explains the many intrinsic benefits of placing trust and responsibility in the hands of employees. Because employees have historically been given a flat exchange of time and energy for income, workplace incentives have often been. Douglas mcgregor spent the end of the 1950’s and the early 1960’s working on his motivation theory.
Many have categorized theory x as an autocratic type of leadership and theory y as democratic style. Theory x and theory y are theories of human work motivation and management. What is theory x and theory y?
Theory x assumes that there is a centralization of authority and very tight control over the employees, but theory y says that the authority should be decentralized and that should be leniency in control. This increasing trend means more and more organizations adopt theory y. Unlike, decentralisation of authority is presumed in theory y, which involves.
This approach believes that employees can be led by giving them fulfilling work. According to theory x, there is complete centralization of authority, in the organisation, i.e. If correlate it with maslow’s theory, we can say that theory x is based on the assumption that the employees emphasize on the physiological needs.
Developed in the 1960s by douglas mcgregor in his book, “the human side of enterprise, 1 theory x and theory y allocate the job of management into two styles. As such, threats of punishment are far less effective in motivating the employee. Figure 2 theory x managers rely heavily on threat and intimidation to gain their employees.
In his 1960 book, the human side of enterprise, mcgregor proposed two theories by which managers perceive and address employee motivation. Theory x works on the idea of punishing people to keep the work going, while under theory y, promotions, rewards, and recognition play an important part. The power lies in the hands of the top executives.
In understanding these management styles, theory x is best defined through the backdrop of theory y, which relies on a managerial approach that uses job satisfaction as its motivation for employees. Douglas mcgregor then arrived at the. Theory x is characterised by tight external control on the employees, whereas theory y features leniency in control.
Each of the viewpoints addresses a different way of meeting each individual. Theory x vs theory y managers. The management theory x is a management style that employs a great level of control, guidance, and involvement from supervisors or team leads.
This type of management style is more common than theory x. And a positive attitude represents liking work or being responsible towards their works. It seems mcgregor himself preferred this management style between theory x and theory y.
This style assumes that employees work with very. Theory y implies that employees look beyond just money and strive for a purpose in what they do. There is no question that theory x and theory y had an incredible impact on management thinking.
Douglas mcgregor's theory x and theory y in his 1960 management book, the human side of enterprise, douglas mcgregor made his mark on the history of organizational management and motivational psychology when he proposed the two theories by which managers perceive employee motivation.he referred to these opposing motivational methods as theory x and. Serhat kurt october 11, 2021. Mcgregor's work was rooted in motivation theory alongside the works of abraham maslow, who created the hierarchy of needs.the two theories.
Theory x and theory y were part of mcgregor’s philosophy of management, which represented a fundamental change in management thought and practice. These differing management styles have been coined in the academic management community as theory x and theory y. [1] if you believe that your team members dislike their work and have little motivation, then, according to mcgregor, you'll likely use an.
The theory x and theory y created by douglas mcgregor in 1950s and developed later in the 1960s. He referred to these two perceptions as theory x and theory y. His major writings are cited along with two volumes which.
Theory x says that people are influence and controlled by reward and punishment system. They were created by douglas mcgregor while he was working at the mit sloan school of management in the 1950s, and developed further in the 1960s.
Lewin’s model is rather simple however other change management theories are based on this model. Stability is the normal state of affairs and change is the unusual.
Transition is the inner movement or journey we make in reaction to a change.

History of change management theory. Ad gain visibility across infrastructure & apps, optimize cloud delivery & spend. Change management literature and its historical development are often used to develop new change frameworks, beyond the ones mentioned here. Lewin’s model of change is divided into three stages of unfreeze, change and freeze referring 3 stages of changes.
The notion that organizational history is objective and oppressive to change is, perhaps, the dominant view in management research. Of organization change, and it has been only recently that organization change has become an interest of scholars. Kurt lewin’s three phase model.
This second stage occurs as we make the changes that are needed. His theory had four basic principles: Change is viewed as an improvement.
1) lewin’s change management model. Change theories p below are samples of both classic and current change theories. These assumptions suggest that because time and history reduce agency, change is very difficult to accomplish because any change effort must face the herculean task of overcoming the past.
Lewin's first venture into change management started with researching field theory in 1921. As a result, this led to the study of management and later the effects that change makes. British people who immigrated to australia.
Lewin’s model is a concept of repeating cycles of three phases. A brief history of change management. These are six of the leading theories that appeared after this event.
Found that even though people were trained on new tools and methods, that there was a motivational issue at play that. In 1948, lester coch and john french jr. We could say that there have been four stages that have marked its development throughout its history.
Was a period of remarkable growth in theories of management, and in the. This model was designed and created by kurt lewin in the 1950s, and it still holds valid today. During this period, the focus was on improving our collective understanding of human beings, how we experience change and how our human systems interact and react.
In this topic you will examine some of the key theories that have influenced change management thinking over the past 100 years. For example, many change managers in healthcare use their own models. What follows, then, is a tracing of the important forerunners of the modern study of organization change:
The model of kurt lewin, one of which we will mention here,. Change management, as a formal discipline, has been around since the 1990’s. However references to change and change management can be found in the psychological literature more than 40 years.
The first era of change management was the period before 1990. In 1948 lester coach and john french studied the motivational issues centered around change initiatives. 1) find the one best way to perform each task, 2) carefully match each worker to each task, 3) closely supervise workers, and use reward and punishment as motivators, and 4) the task of management is planning and control.
The evolution of change management: Change in an honest manner (monaghan, 2009; Change has seen some big changes over the last 60 years.
Lewin was a physicist and social scientist who. It’s a key turning point in the history of management. This era provided crucial insights, research and frameworks for understanding successful change.
Lewin shows how, using field theory, the insights from these experiments involving children can be used to change the behavior of managers and political leaders. From lewin's 3 step change theory of 'unfreeze, make changes, refreeze' to a current expectation that organisations should never ". The first example concerns the lewin et al.
These, however, are still based on change management theories such as those mentioned here. The roots of change management stretch back to world war ii and the mass mobilization of soldiers. Lewin’s change management model is one of the most popular and effective models that make it possible for us to understand organizational and structured change.
5 years later, lewin would begin a series consisting of about 20 articles to explain field theory. Kurt lewin was aware that change is not an event, but rather a process. People are 'unfrozen' and moving towards a new way of being.
Set your study reminders we will email you at. It was him that first stressed, through his research, the importance of communication and leadership in ensuring that an organisation would reach its objectives. He called that process a transition.
Prosci asserts that change management has undergone major changes over the last forty years. The industrial revolution sparked great debate about management theory. This provides further examples of field theory and behavioral change.
Before 1990, for change management, they took into account only psychology and human behavior. Management theories have been intensively developed over the last decades [5].it is possible to historically demarcate the classical approaches (the bureaucratic or. Initially, taylor was very successful at improving production.
Kurt lewin was a social scientist who researched learning and social conflict. The origins of the concept of change management can be traced down to the birth of the human relations movement and elton mayo‘s work. Theory and practice of change management study reminders.
Scientific management the hawthorne studies industrial psychology survey feedback sensitivity training sociotechnical systems Ad gain visibility across infrastructure & apps, optimize cloud delivery & spend. Decision theory (1960s) the decision theory method of change management suggested that individuals “satisfice” when they make decisions.
Human resource policies are continuing guidelines on the approach of which an organization intends to adopt in managing its people. By emphasizing “strong culture”, hrm is.

PPT Chapter 1 Nature of Human Resource Management PowerPoint
These fields comprise the branch of philosophy called axiology.

Ethical issues in human resource management wikipedia. Since, the success or failure of the business totally depends upon the ethical behavior shown by the managers in the organization. Explain what is meant by ethical behavior at work. Ethical issues in human resource management jastinder pal singh.
Hr in the middle ethics in hr management employers association of new jersey. In this connection, schuler et al. Globalization, economic and legal environment, workforce diversity resulting from both globalization and.
Discuss important factors that shape ethical behavior at work. The tight labor market continues. Besides encouraging employee collaboration and accountability, here are the essential functions of ethics in human resource management.
Ethical demand in the workplace is the concern of the human resource management in the present context (jack, greenwood, and schapper, 2012). Ethics seeks to resolve questions of human morality by defining concepts such as good and evil, right and wrong, virtue and vice, justice and crime. For instance, policies related to minimum wage and employee overtime pay show.
The field of ethics, along with aesthetics, concerns matters of value; Ethics in human resource management (hrm) meaning of hrm hrm can be understood in simple terms as employing people, developing their resources, utilising, maintaining and compensating their services in tune with the job and organizational requirements with the view to contribute to the goals of the organization, individuals and the society. Strategic human resource management can be define as a perfect way to make effective use of the planning and align it with the organizational goals, use a coherent approach in managing and people at the workplace, to develop a system based on the workforce strategy and employment policy of the firm.
Human resource management (hrm) is adopted by many companies because of its benefits. Despite all the statements of the proponents of human resources management (hrm), they can be criticized for using alternative and complex forms of “control of methods of subordination” in attempts to justify the need to build workers’ attachment to the needs. Concept of human resouce management ppt jaanviarora1.
Discussions in ethics in hrd stem from employee relationships and whether or not there can be a standard for the same. According to winstanley, woodall and heery (1996), ‘ethics is a special branch of philosophy that focuses on the questions related to morality, that is concepts such as good and bad, right and wrong ; Expatriate failures continue to be a significant problem for many international firms.
Employee rights and duties and freedom and discrimination at the workplace are issues discussed and covered by most texts on the topic. Business ethics deals with the degree and extent of morality to be used in business (george. These numbers suggest you’ll likely encounter ethical dilemmas in your workplace.
Courageous follower and leader, 2006). Hr ethics helps you conduct business in line with the employment law due to fair employment practices. Working alone or in groups to analyze the ethical issues and recommend solutions
Therefore, we can say that it is a special branch of management where ethics play a crucial role. But at the same time, various challenges and issues may emerge in front of managers of human resource department while performing their duties. Nevertheless ethics in human resource management has become a perennial debate of late!
Unethical practices spurred more than half of the largest bankruptcies in the past 30 years, like enron, lehman brothers, and worldcom, and can take a larger economic toll, estimated at $1.228 trillion, according to the society for human resource management. They represent specific guidelines to hr managers on various matters concerning employment and state the intent of the organization on different aspects of human resource management such as recruitment, promotion, compensation,. The university of west alabama fafter studying this chapter, you should be able to:
Business failures in the international arena may often be linked to poor management of human resources, and. Human resource management (hrm or hr) is the strategic approach to the effective and efficient management of people in a company or organization such that they help their business gain a competitive advantage.it is designed to maximize employee performance in service of an employer's strategic objectives. Chapters 3, 4, 6 and 14.
Any capable hr manager would work on these issues and challenges to prevent the organizational activities from being. Most frequently mentioned challenges of modern hrm are: Thus, legge, (legge, 1989) emphasizes:
Ethics or moral philosophy is a branch of philosophy that involves systematizing, defending, and recommending concepts of right and wrong behavior. Hrm concerns human issues, especially those related with compensation, development, industrial relations. Human resource management (hrm) deals with work force management, manpower planning and other employee related activities in an organization.
Human resources is the set of people who make up the workforce of an organization, business sector, industry, or economy.a narrower concept is human capital, the knowledge and skills which the individuals command.similar terms include manpower, labor, personnel, associates or simply: Describe at least four specific ways in which hr management can influence ethical behavior at work. These ethics originate from individuals, organizational.
Ethics, justice and fair treatment of employees. [need quotation to verify] human resource management is. Hrm at any level is important to strategy implementation;
As a field of intellectual inquiry, moral philosophy i… Business ethics (also known as corporate ethics) is a form of applied ethics or professional ethics, that examines ethical principles and moral or ethical problems that can arise in a business environment.it applies to all aspects of business conduct and is relevant to the conduct of individuals and entire organizations. When it comes to acquiring top talent, the game has changed.
In today's business environment human resource professional responsibilities and roles are increasingly more extensive than that of.
Leaders could be seen as addressing broader concerns, such as employee experience, productivity, workplace culture, and organizational development. They take the time to detail a plan, layout the parts, and see it followed through.

Leadership vs Management Is One Better Than the Other? Core Aspect
The primary difference between management and leadership is that leaders don’t necessarily hold or occupy a management position.

Difference between leadership and management with examples. As such, they focus on projects, tasks and due dates, simply handing out assignments to their employees and making sure they get done. There are people who talk about the two systems as interchangeable, while many believe the. Management tends to focus more on work, how it is organised, and the specific tasks.
But, one thing is for certain: Unlike managers, leaders are followed because of their personality, behavior, and beliefs. Leaders break the rules for the sake of the organization they are leading.
For example, if your company has set the goal to reduce monthly customer. When it comes to understanding the difference between leadership and management, it may be helpful to think of a map. Leading by example, inspiration and empowerment are all parts of being a leader.
What remains is an abstraction of two concepts with no consensus and little application. While management deals with the technical dimension in an organization or the job content; The difference between leadership & management with examples.
Leadership deals with the people aspect in an organization. People often mistakenly equate leadership with management, but there are fundamental differences between the two; This is where hiring the right people, with experience you can draw on, can set you apart from the competition.
Let’s explore this idea more in depth. In fact, you don’t have to have the title of manager or have direct reports to be a. A leader can be anyone.
Management involves a focus on executing functions, whereas leadership is about motivating people. Here are three ways leaders and managers might approach the same situation differently in order to best support their team. Although some leadership and management skills overlap, it's important to know the distinctions between these two roles.
Leadership places more of a focus on achieving goals and team motivation and empowerment, allowing leaders to get the best out of everyone for a mutual benefit. Explanation and examples of differences it is appropriate here briefly to explain, and give examples of, the differences between management and leadership. For example, you tell your managers that you want to focus on enhancing employee benefits this quarter.
“management is efficiency in climbing the ladder of success; The contention that leadership and management are different is an example of proposition and belief not representing reality. Leadership prefer the give credit to those whom they worked together to achieve the goals.
The first difference you'll find between management and leadership is in their minds. As the business grows, the focus shifts to scalability and organizing people around processes and systems. For example, some managers do not practice leadership, while others lead without a managerial role.
While management measures/evaluates people by their name, past records, present performance; The following are seven of the most significant differences between leading and managing at work: A leader is responsible for choosing a destination and the overall direction, while a manager shares the specific turns you need to make to get from point a to point b.
8 rows some examples of leaders, which are born in india are mahatma gandhi, amitabh bachchan, kiran. Management explore the main differences between leadership and management, including styles, models and philosophies. Meanwhile, leaders tend to focus more on motivating teams.
Leaders are driven by vision, and managers execute it. Leaders and managers have a lot in common, but they frequently approach situations in different ways. Managers set the rules to be followed and make sure they are followed.
Managers may be viewed as more practical and focused on implementation; While leadership is still important, management is key in this phase. 8 rows in an organizational setup, a manager is an important link between the firm and its.
When it comes to the organization’s culture, the difference between leadership and management is that leaders define and shape the culture. Management involves following the rules closely, while leadership often entails creativity and innovation. There are tons of different competencies that are necessary to be an effective leader or manager.
They have a grasp of how long tasks take and why because they dig in and get familiar with their team’s work. Leadership is often based on a mission, while management is often based on a specific task being completed. Leaders, on the other hand, always keep at the forefront of their.
This is by no means an exhaustive list. And, in an ideal world, there will also be plenty of overlap between the two. However, no scientific evidence exists to support the described differences between leadership and management;
Simply put, a leader doesn’t have to be an authority figure in the organization; Leadership sees and evaluates individuals as having potential for things that can’t be measured, i.e. Rather than trying to dispel these perceptions, we should be taking a deeper look at the “differences” between management.
A manager is generally someone who is selected or appointed within an organization. Develop an understanding of their key characteristics. They are separate and distinct skill sets.
3 differences between leaders and managers.
