Harrison (1972) presents a model of culture, known as harrison’s model of culture that divides organisational cultures into the four categories: Power in a role culture is determined by a person’s position (role) in the.

Charles Handy Organizational Culture Business powerpoint templates
This culture is all about getting the right people together and then letting them get on with the task in hand.this type of culture is all about team work and because of this is lead by expert power, the people with more knowledge and experience will tend to be the people who lead this type of culture in an organisation and bring the teams together to work towards the common.
Power role task and person culture. Schein (1985) used three levels to explain organisational culture, namely artefacts, values and basic underlying assumptions. They are highly controlled, with everyone in the organization knowing what their roles and responsibilities are. A power culture is usually a strong culture, though it can swiftly turn toxic.
Power is shared between the people who set up the business, a partnership. 2) there are three main organizational structures: Power derives from a person's place or role within a highly structured organization.
A centralised culture which focuses on key decision makers. It will be also explaining what handy meant by the four types of culture which are power, role, task and person culture with an organisation example with each. Role cultures are highly bureaucratic with detailed rules about how people and departments interact with each other, customers and vendors.
It is a cluster, there to help the individuals to profit from themselves. It is also referred to as. In role culture organisations formal.
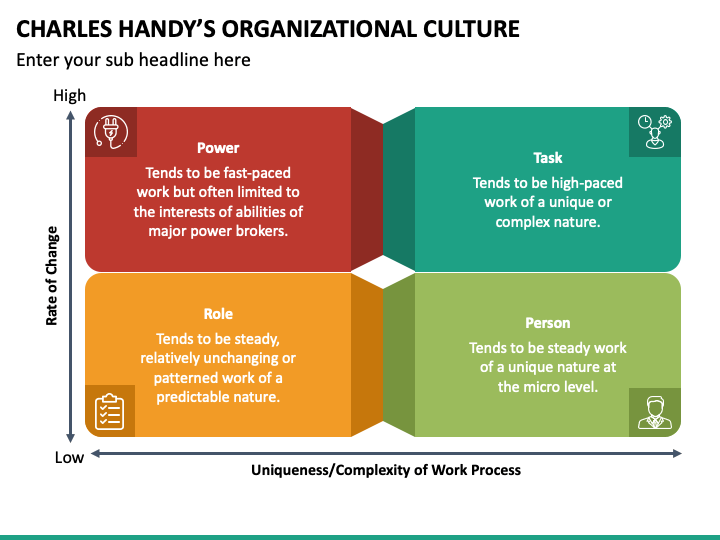
In a role culture power comes from the personal position whereas in the task culture the power is derived from the team. The four types of culture he identified were: Charles handy’s types of organisational culture power culture role culture power culture is associated with autocratic leadership.
Due to the importance of given tasks, and the number of small teams in play, a matrix structure is common. Role, task, power, and person cultures. In this type of culture, horizontal structures are most applicable.
Compare and contrast them and explain how they are different and use examples to illustrate. Ultimately, the combination of the two dimensions results in four organisational cultures: In business of this type, the organizational culture is oriented to the power exercised and maintained by only a few leaders who end up influencing.
Power, role, task and person. Power is concentrated in the centre of the. The principles and beliefs of any organization form its culture.
According to charles handy, there are four types of cultures from which any one of these types of culture can be seen in a particular business organization. The power culture, the role culture, the task culture, and the person or support culture. Handy believed that there are four main types of organizational culture which can be identified by the extent to which an organisation is both formalized and centralized.
Among these four types of culture described in the previous part of this report such as power, role, task and person culture, we are to use the role culture in case of nestle. Role culture, power culture, person culture and task culture: Such organisations typically form hierarchical bureaucracies where power derives from a person's position and little opportunity exists for expert power.
Organizations with a role culture are based on rules. Power shifts depending on who is in the team, the nature of the problem or the stage in the task’s completion. For instance, the power culture relies on a few individuals at the center to make decisions that.
There are four organisational cultures which are power, role, task and person culture. The most crucial types of culture mentioned by the scholar include person, power, role, and task cultures, respectively. The first advantage is the specialization where each.
No two organizations can have the same culture and it is essential for the employees to adjust well in their organization’s culture to enjoy their work and stay stress. Are formed to solve particular problems. An example of this type of culture is architects or social groups.
Lastly the blog will be finishing with what i believe the problems are of trying to classify culture into one of the four types of culture by handy with a conclusion to finish off the blog. The paper examines the advantages and disadvantages associated with each of the cultures that were identified by charles handy. Charles handy, a leading authority on organisational culture, defined four different kinds of culture:
Handy outlined four types of culture: May come under stress if a business grows and cannot all be run from the. Power culture power culture tends to have one or a minor group of individuals making decisions and it is normally.
Handy’s approach may help you understand why you have been more. Power is derived from membership in teams that have the expertise to execute a task. The difference between role culture and task culture is that one is individual and the other one is teamwork.
According to irish philosopher charles handy, specialized in organizational behavior, there are four different types of organizational culture: May occur in small businesses where the founder dominates; The task, and completion of the task, is the most important thing!
Scholtz (1987) identified five primary culture typologies, namely stable, reactive, anticipating, exploring and creative. As this type of organisation is run by the individuals, it has no real power to get rid of someone in the organisation; Power, role, task, and person.
The short revision video below explains handy's model and there are some study notes underneath. If you get the right mix of people, leadership and governance structures, it can be very powerful. The organization culture decides the way employees interact amongst themselves as well as external parties.
Organisations with role culture tend to be reliant on formal rules and regulations. Classification, namely power, role, task and person cultures. Power, role, task and person.
This is what a good matrix organisation looks like. Features of these types of culture include: Task culture person culture groups are formed to solve particular problems, and lines of communication are similar to a matrix structure (see 2.2).
One person controlling every area of business.